History of HIV /
Sejarah HIV
HIV originated from a form of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus found in chimpanzees (SIVcpz) in the early 1900s. The first known case of HIV was later discovered from a preserved blood sample of a man who passed away in the Congo in 1959. First warning was issued by The United States Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) about a relatively rare form of pneumonia among a small group of young homosexual men in Los Angeles, which was later confirmed to be related to AIDS.
Penyakit HIV berasal dari Simian Immunodeficiency Virus yang dijumpai dalam cimpanzi pada awal 1900. HIV telah ditemui dalam sampel darah seorang penyakit yang telah meninggal dunia pada tahun 1959. Maka, amaran pertama terhadap sejenis pneumonia dalam kalangan sekumpulan lelaki homoseksual telah dikeluarkan oleh CDC, di mana penyakit tersebut telah dibuktikan berkaitan dengan AIDS.
What Is HIV? /
Apa Itu HIV?
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a virus that weakens the immune system, making the human body susceptible to infections.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) merupakan suatu virus yang melemahkan sistem imun, menyebabkan pesakit mudah mendapat jangkitan kuman.
Key Population At Risk / Populasi utama yang berisiko tinggi
- People who inject drugs (PWID)
Individu yang menyuntik dadah - Female sex workers (FSW)
Pekerja seks wanita - Men who have sex with men (MSM)
Lelaki yang berhubungan seks dengan lelaki - Transgender women (TG)
Wanita transgender

HIV infection can progress to AIDS (late stage) if left untreated.
Jangkitan HIV boleh menjadi AIDS (tahap akhir) sekiranya tidak dirawati.
AIDS is defined as a number of life-threatening infections and illnesses
that occur when your immune system has been severely damaged by HIV.
AIDS didefinisikan sebagai beberapa jangkitan dan penyakit yang berlaku apabila
sistem imun pesakit telah dirosakkan oleh HIV.
Mode of Transmission /
Cara Penyebaran Jangkitan
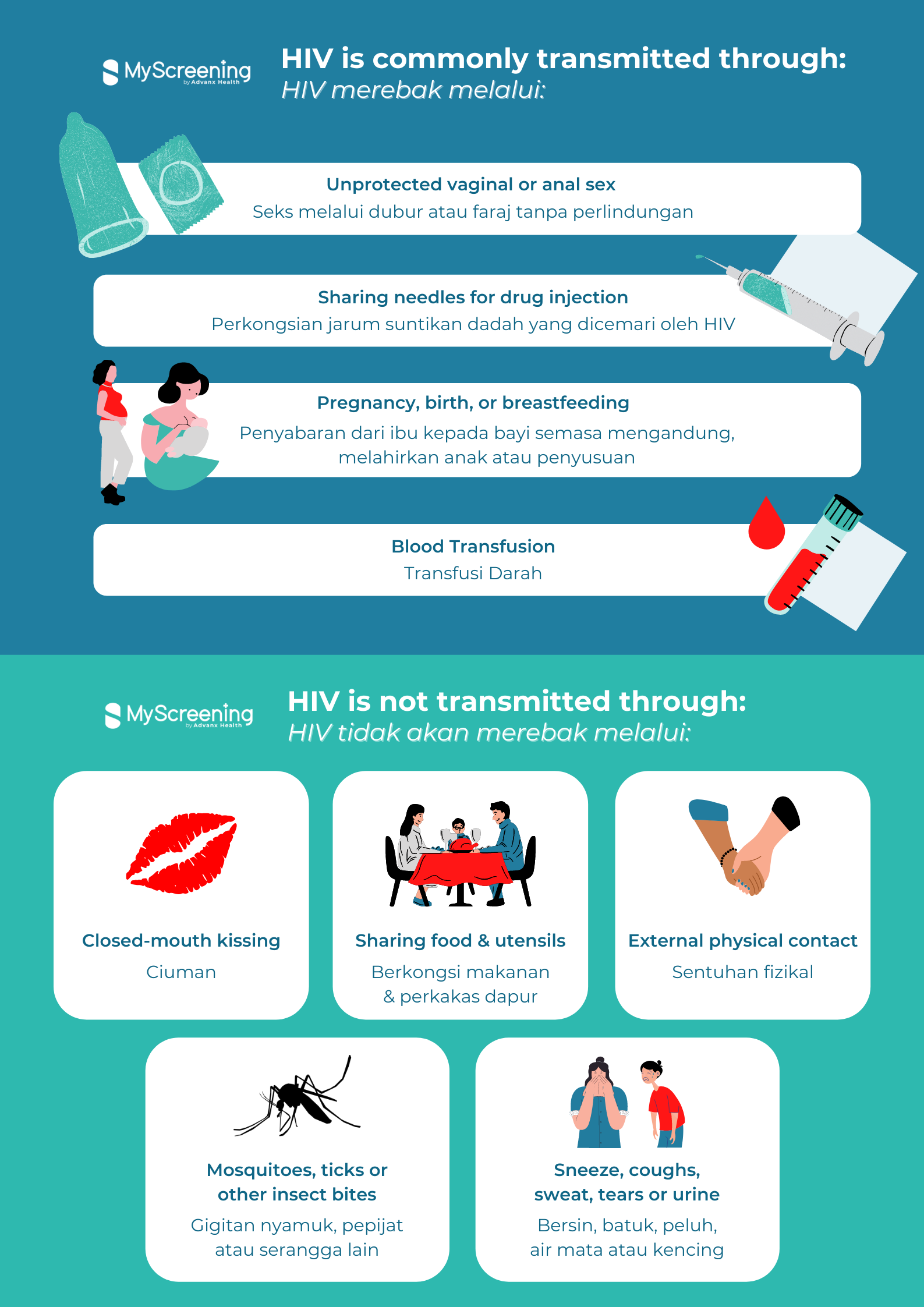
HIV Is Transmitted Through
HIV (punca HIV) Merebak Melalui
- Unprotected vaginal or anal sex with an infected person
Seks melalui dubur atau faraj tanpa perlindungan dengan pesakit HIV - Sharing needles contaminated with HIV for drug injections
Perkongsian jarum suntikan dadah yang dicemari oleh HIV - From HIV positive mother to child during pregnancy, birth or breastfeeding
Penyebaran dari ibu yang dijangkiti HIV kepada bayi semasa mengandung, melahirkan anak atau penyusuan - Transfusion of blood contaminated with HIV
Transfusi darah yang mengandungi HIV
HIV Is Not Transmitted Through
HIV Tidak Merebak Melalui
- Closed-mouth kissing with HIV positive person
Ciuman - External physical contact such as shaking hand and hugging
Sentuhan fizikal seperti berjabat tangan dan memeluk - Sharing food and utensils
Perkongsian makanan dan perkakas dapur - Sneeze, coughs, sweat, tears or urine
Bersin, batuk, peluh, air mata atau kencing - Mosquitoes, ticks or other insects bites
Gigitan nyamuk, pepijat atau serangga lain
HIV Symptoms & Stages of HIV /
Gejala & Tahap HIV
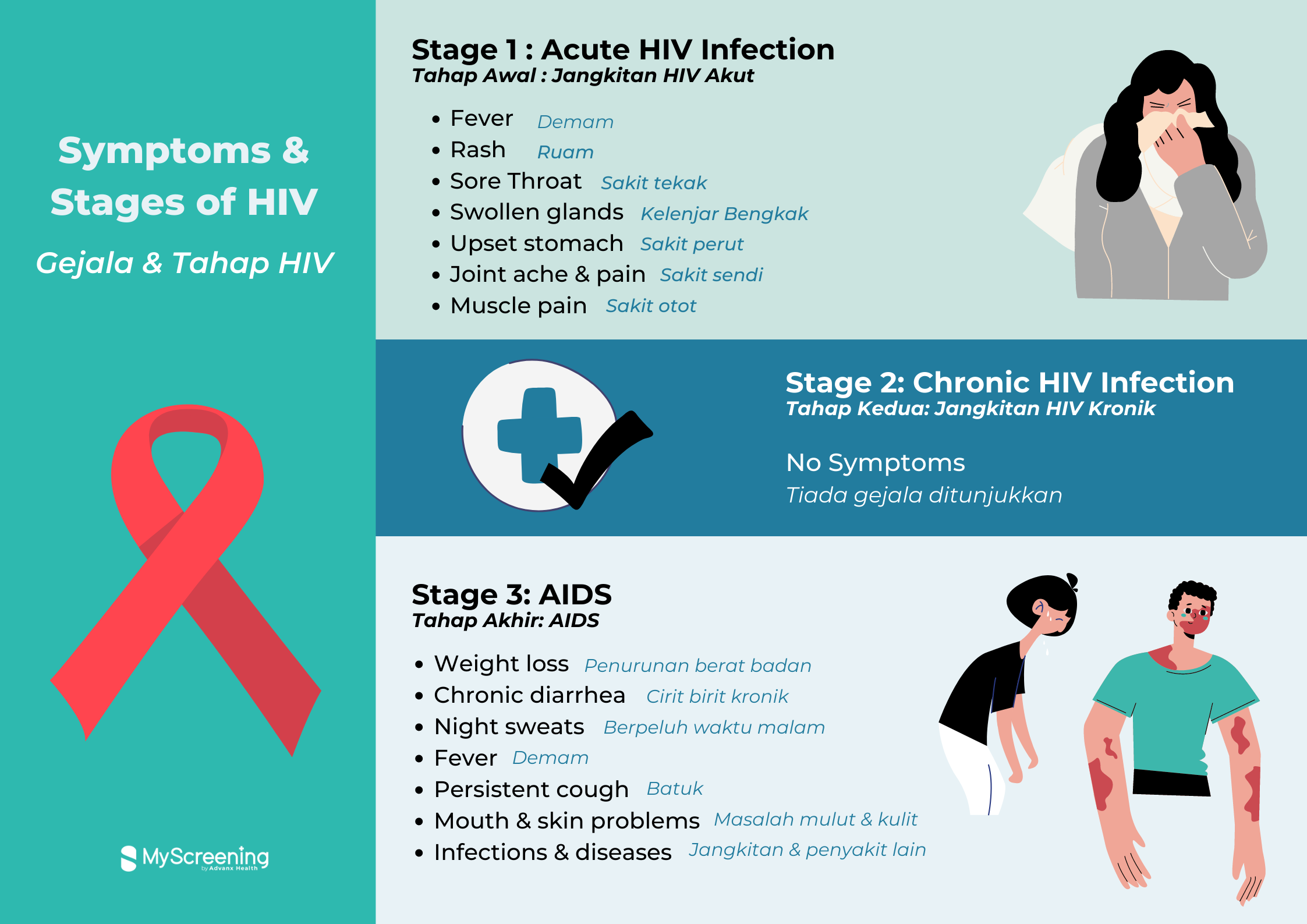
Within 2-4 weeks after infection, some may not exhibit any HIV symptoms, some may experience flu-like HIV symptoms such as fever, rash, sore throat, swollen glands, headache, upset stomach, joint aches and pains and muscle pain.
During this stage, HIV multiplies rapidly, spreads throughout the body and attacks infection-fighting cells, also known as CD4 cells. However, if you experience any of the HIV symptoms stated, it does not confirm HIV infection, be sure to get tested if you are in doubt. In Malaysia, HIV Screening test is free of charge for the public at government clinics and hospitals. Rapid at home tests can also be purchased over the counter or online at an affordable price.
Dalam jangka masa 2-4 minggu selepas dijangkiti, sesetengah individu mungkin tidak menunjukkan sebarang gejala manakala sesetengah individu mungkin mengalami gejala selesema seperti demam, ruam, sakit tekak, kelenjar bengkak, sakit kepala, perut, sendi dan otot.
Pada tahap ini, HIV membiak secara cepat, merebak kepada seluruh badan dan menyerang sel yang melindungi badan daripada jangkitan iaitu sel CD4. Walau bagaimanapun, sekiranya anda mengalami sebarang gejala yang dinyatakan tidak bermakna anda mendapati jangkitan HIV. Jalani ujian saringan sekiranya anda berasa mungkin dijangkiti HIV. Ujian saringan HIV adalah percuma kepada rakyat Malaysia di klinik kesihatan dan hospital umum. Kit ujian segera turut boleh diperolehi dari kedai farmasi atau secara atas talian dengan harga yang berpatutan.
In this stage, multiplication of HIV proceeds at a very low level, hence people with chronic HIV infection may not experience any symptoms
Pada tahap ini, pembiakan HIV diteruskan pada tahap yang rendah, maka pesakit mungkin tidak mengalami sebarang gejala.
The final stage of HIV infection is known as AIDS, where CD4 cells count is less than 200 cells/ml or viral count more than 30 000 copies/ml. In other words, immune systems are severely damaged that they can no longer protect the body from infections.
Therefore, AIDS patients are at risk of opportunistic infections, which are infections that occur more frequently or more severe in people with weakened immune systems, for example, pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP). The symptoms include weight loss, chronic diarrhea, night sweats, fever, persistent cough, mouth and skin problems, regular infections and serious illness or diseases.
Tahap akhir jangkitan HIV, juga dikenali sebagai AIDS, di mana bacaan sel CD4 adalah kurang daripada 200 sel/ml atau bacaan virus adalah melebihi 30 000 copies/ml. Ini bermaksud sistem imun telah dirosakkan dan gagal melindungi tubuh badan daripada jangkitan.
Oleh sebab itu, pesakit mempunyai risiko yang tinggi bagi jangkitan oportunistik iaitu jangkitan yang sering berlaku pada individu yang mempunyai sistem pertahanan badan yang lemah, contohnya, pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP). Gejala AIDS termasuk penurunan berat badan cirit-birit kronik, berpeluh pada waktu malam, demam, batuk, masalah kulit dan mulut, jangkitan dan penyakit lain.
HIV in Malaysia /
HIV di Malaysia
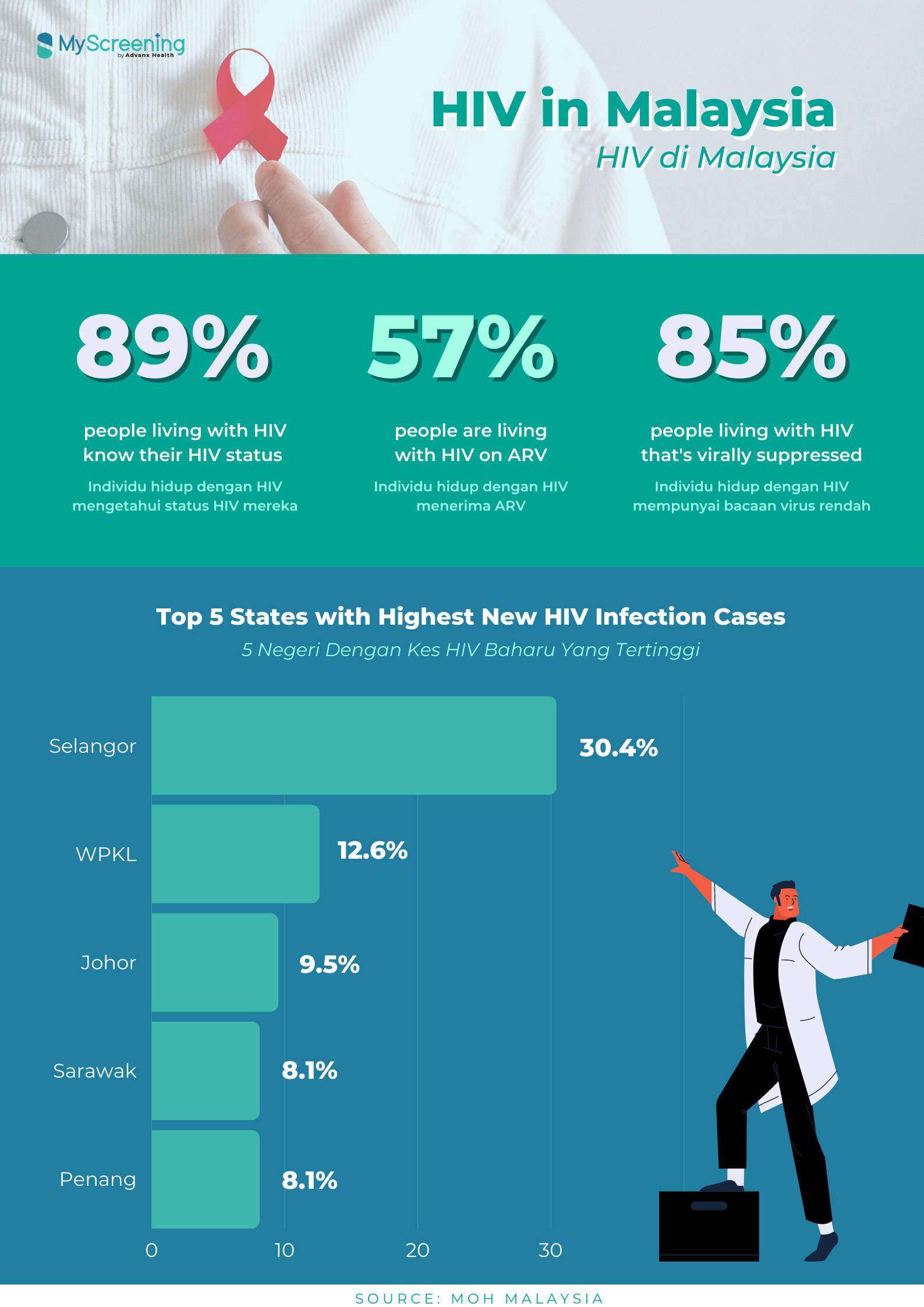
According to Global AIDS Monitoring 2020, it is estimated that around 87,000 people are living with HIV in Malaysia in 2019. Selangor (30.4%), Kuala Lumpur (12.6%) and Johor (9.5%) were the major contributors to new HIV cases, predominantly among males and people aged 20-39 years.
Among them, 89% of the people living with HIV know their HIV status, in which 56% of them were receiving antiretroviral therapy and 85% of them had their viral load under control. In the past decade, the proportion of sexual transmission overtook sharing of drug injection needles as the main mode of transmission among people diagnosed with HIV infection in Malaysia.
Menurut Laporan Global AIDS Monitoring 2020, individu yang hidup dengan HIV di Malaysia adalah dijangka seramai 87,000 pada tahun 2019. Selangor (30.4%), Kuala Lumpur (12.6%) and Johor (9.5%) menyumbang kepada majoriti kes baharu HIV, terutamanya dalam kalangan lelaki dan golongan berumur 20-39 tahun.
Sebanyak 89% individu yang hidup dengan HIV mengetahui status HIV mereka, sebanyak 56% menerima terapi antiretroviral (ART) dan sebanyak 85% mempunyai bacaan virus yang rendah.
How To Prevent HIV? /
Bagaimana Untuk Mencegah HIV?
Types of HIV Preventive Medications /
Jenis-jenis Ubat Pencegahan HIV
PEP (Post Exposure Prophylaxis) is a combination of prevention medications given to a patient after a possible HIV exposure, to stop the HIV virus from replicating in the patient's body.
PEP merupakan kombinasi ubat pencegahan yang diberi kepada pesakit setelah potensi pendedahan HIV untuk menghentikan replikasi virus HIV dalam tubuh badan pesakit.
The patient is HIV-negative and they may have been exposed to someone with HIV positive. The exposure could have happened if:
PEP diberi kepada pesakit negatif HIV, dan mempunyai potensi pendedahan kepada pesakit HIV. Pendedahan boleh berlaku jika:
- Condom broke during sex
Kondom pecah semasa seks - Through sharing of needles/syringes
Perkongsian jarum - The person was sexually asaulted.
Seseorang dirogol
PEP is an emergency medication and it is not intended to replace other HIV prevention methods. This medication must be taken soonest or within 72 hour of exposure. This is because the effectiveness of PEP reduces over time, therefore it is recommended to be taken no later than 72 hours after exposure. As instructed, PEP must be taken for 28 days to allow it to work at an optimum level.
PEP ialah ubat kecemasan dan tidak boleh menggantikan kaedah pencegahan HIV yang lain. PEP perlu diambil secepat mungkin atau dalam tempoh 72 jam selepas pendedahan HIV. Hal ini kerana keberkesanan PEP akan menurun dari semasa ke semasa. PEP perlu diambil selama 28 hari agar berkesan pada tahap optimum.
Note!
Peringatan
- If you miss the dose do not double up the dose
Jangan menggandakan dos jikalau terlepas makan - If you happen to miss a dose and remembered within 24 hours, take the next one as soon as you remember
Mengambil dos seterusnya secepat mungkin jikalau terlepas makan dalam tempoh 24 jam - If you happen to miss PEP for 48 hours, it will be discontinued as it won't be able to work
PEP tidak berkesan jika terlepas makan dalam masa 48 jam
Fact
Fakta
According to a study published in 1997 in New England Journal of Medicine, treatment was unsuccessful when PEP was stopped before 28 days. This was a case-control study done among healthcare workers.
Menurut kajian yang diterbitkan pada tahun 1997 di New England Journal of Medicine,rawatan PEP gagal apabila dihentikan sebelum 28 hari.Ini merupakan kajian kawalan-kes yang dijalankan antara pengamal perubatan.
Some of the commonly known side effects of PEP include:
Antara kesan sampingan yang biasa dikenali ialah:
- Nausea
Loya - Headache
Sakit kepala - Tiredness
Rasa penat
PEP therapy may not be effective or fail in providing you the protection you need if you:
Terapi PEP tidak efektif atau gagal memberi perlindungan kepada anda jika anda:
- Fail to start PEP within the timeframe of 72 hours
Gagal untuk bermula PEP dalam jangka masa 72 jam - Do not complete the 28 day course as advised by the physician or skipping/missing the medication
Gagal menghabiskan PEP 28-hari seperti dinasihatkan oleh pengamal perubatan; atau terlepas makan - Have a HIV strain that is resistant to the drugs used in PEP
Mempunyai strain HIV yang mempunyai rintangan kepada ubat-ubatan PEP - Fail to follow HIV prevention methods, therefore exposing yourself to HIV, for example by having unprotected sex while on PEP
Gagal untuk mengikuti kaedah atau metod pencegahan HIV; mendedahkan diri sendiri kepada HIV. Contohnya, melakukan seks secara tidak selamat ketika dalam rawatan PEP
In Malaysia only a Medical Doctor is authorized to prescribe PEP medication to patients.
Di Malaysia, hanya doktor perubatan sahaja yang boleh memberikan rawatan dan ubat PEP kepada pesakit.
PrEP(Pre-exposure prophylaxis) is a highly effective prevention medication for HIV. Unlike PEP, PrEP medication is taken before a potential exposure to HIV. This is to prevent and protect you against HIV.
PrEP merupakan ubat pencegahan HIV yang amat berkesan. PrEP diambil sebelum potensi pendedahan kepada HIV. Ubat ini melindungi dan mengelakkan anda daripada HIV.
In order to be eligible to take PrEP you will first need to be:
Anda layak mengambil PrEP jika anda:
- Tested negative for HIV negative
Disahkan negative untuk HIV - Free from sexually transmitted diseases (STD) such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea and syphilis
Bebas daripada jangkitan kelamin (STD) yang lain seperti klamidia, gonorea, dan sifilis - Do a kidney function test which will be conducted by your healthcare provider
Menjalankan ujian fungsi buah pinggang oleh pengamal perubatan
Although PrEP is taken to protect you against HIV but other preventive steps should also be taken such as:
Walaupun PrEP diambil untuk melindungi anda daripada HIV, langkah pencegahan juga perlu diambil seperti:
- Proper usage of condom during sexual intercourse
Penggunaan kondom yang betul semasa pergaulan seks - If your partner is HIV positive, make sure he/she is taking the necessary treatment
Memastikan pasangan menjalankan rawatan jika disahkan positif HIV - Awareness of HIV
Kesedaran terhadap HIV
According to statistics gathered from Center for Disease Control (CDC), if PrEP treatment is taken as prescribed it is able to prevent HIV by :
Menurut statistik daripada Center for Disease Control (CDC), penggunaan PrEP yang ditetapkan dapat mencegah HIV:
- About 99% by sexual intercourse
Sekitar 99% dari pergaulan seks - At least 74% by sharing of injectable/ needle sharing
Sekurang-kurangnya 74% dari perkongsian jarum
If you are someone who is HIV-negative, taking PrEP can protect you from getting HIV if:
Untuk seseorang yang negatif HIV, pengambilan PrEP dapat melindungi anda dari HIV jika:
- You had a vaginal or anal sex in the last 6 months and;
Anda melakukan seks melalui dubur atau faraj dalam 6 bulan lepas dan ; - You have had sex with someone with unknown HIV status
Anda melakukan seks dengan seseorang yang tidak mengetahui status HIV - You have HIV-positive sexual partners
Anda mempunyai pasangan seksual yang disahkan positif HIV - You have a confirmed diagnosis of sexually transmitted disease in the last 6 months
Disahkan mempunyai jangkitan seksual dalam 6 bulan lepas - You have multiple sex partners
Anda mempunyai banyak pasangan seksual - You share injectables/needles with drugs with someone of HIV positive
Anda berkongsi jarum dengan pesakit HIV positif
Some of the common side effects of taking PrEP include:
Antara kesan sampingan pengambilan PrEP adalah:
- Nausea
Loya - Headaches
Sakit kepala - Weight loss
Penurunan berat badan
After starting on PrEP you are advised to visit the doctor every three months so that proper screening can be done to check for your HIV and STD status. At the same time, the doctor will assess for any potential side effects due to the PrEP medication.
Setelah bermulanya PrEP, anda dinasihatkan untuk berjumpa dengan doktor setiap tiga bulan untuk menjalankan saringan HIV dan STD. Dalam masa yang sama, doktor anda akan menilai jika adanya kesan sampingan pengambilan PrEP.
Your healthcare provider would be able to advise you on the duration of taking PrEP. According to studies it can be taken daily, on-demand or periodically. Daily intake of PrEP will be suitable for someone who has multiple sex partners and have a busy sex life as there maybe a potential exposure to HIV.
Pengamal perubatan dapat menasihatkan anda tempoh pengambilan PrEP .Menurut kajian, PrEP boleh diambil setiap hari, diperlukan, atau, secara berkala. Pengambilan PrEP secara setiap hari lebih sesuai untuk seseorang yang mempunyai ramai pasangan seksual serta aktif dalam seks kerana mereka lebih cenderung untuk didedahkan kepada HIV.
In Malaysia only a Medical Doctor is authorized to prescribe PrEP medication to patients.
Di Malaysia, hanya doktor perubatan dapat memberi ubat dan rawatan PrEP kepada pesakit.
Need PrEP or PEP education?
Contact us at [email protected] to find out more!
Hubungi kami melalui [email protected] bagi maklumat lanjut tentang PrEP atau PEP!
HIV Diagnosis /
Diagnosis HIv
HIV can be detected through a number of testing methods that are usually done by taking a patient's blood. These HIV tests that are able to detect HIV are as follows:
Cara ujian HIV boleh dibuat melalui beberapa kaedah ujian yang biasanya dilakukan dengan mengambil darah pesakit. Ujian HIV yang dapat mengesan HIV adalah seperti berikut:
This HIV test detects antigens from HIV and antibodies towards HIV in the body. Antibodies are produced when you are exposed to an infection. Antigens on the other hand are foreign substances that activate your immune system. If you have HIV, antigen p24 will be detected before the antibodies are formed.
There are two antigen/antibody tests that can be done
- In the laboratory that involves taking blood from the vein
This test can detect HIV infection within 18 to 45 days after exposure
- Rapid test using blood from a finger prick
This test can only detect HIV after 18 to 90 days after exposure
Ujian HIV ini mengesan antigen daripada HIV dan antibodi terhadap HIV di dalam badan. Antibodi dihasilkan apabila anda terdedah kepada jangkitan. Antigen sebaliknya adalah bahan asing yang mengaktifkan sistem imun anda. Jika anda mempunyai HIV, antigen p24 akan dikesan sebelum antibodi terbentuk.
Terdapat dua ujian antigen/antibodi yang boleh dilakukan
- Di makmal yang melibatkan pengambilan darah dari vena
Ujian ini boleh mengesan jangkitan HIV dalam tempoh 18 hingga 45 hari selepas pendedahan
- Ujian pantas menggunakan darah dari tusukan jari
Ujian ini hanya boleh mengesan HIV selepas 18 hingga 90 hari selepas pendedahan
This test detects antibodies to HIV in your blood or oral fluid. Antibody tests that use blood from veins can detect faster after infection than tests using blood from a finger prick or oral fluid. Antibody tests are the most rapid test which use the rapid test method. The test results are ready within 30 minutes or less. HIV antibody tests detect HIV 23 to 90 days after being infected. Premarital testing uses this type of test.
Ujian ini mengesan antibodi kepada HIV dalam darah atau cecair mulut anda. Ujian antibodi yang menggunakan darah daripada urat boleh mengesan lebih cepat selepas jangkitan daripada ujian menggunakan darah daripada tusukan jari atau cecair mulut. Ujian antibodi adalah ujian paling pantas yang menggunakan kaedah ujian pantas. Keputusan ujian siap dalam masa 30 minit atau kurang. Ujian antibodi HIV mengesan HIV 23 hingga 90 hari selepas dijangkiti. Ujian pranikah menggunakan ujian jenis ini.
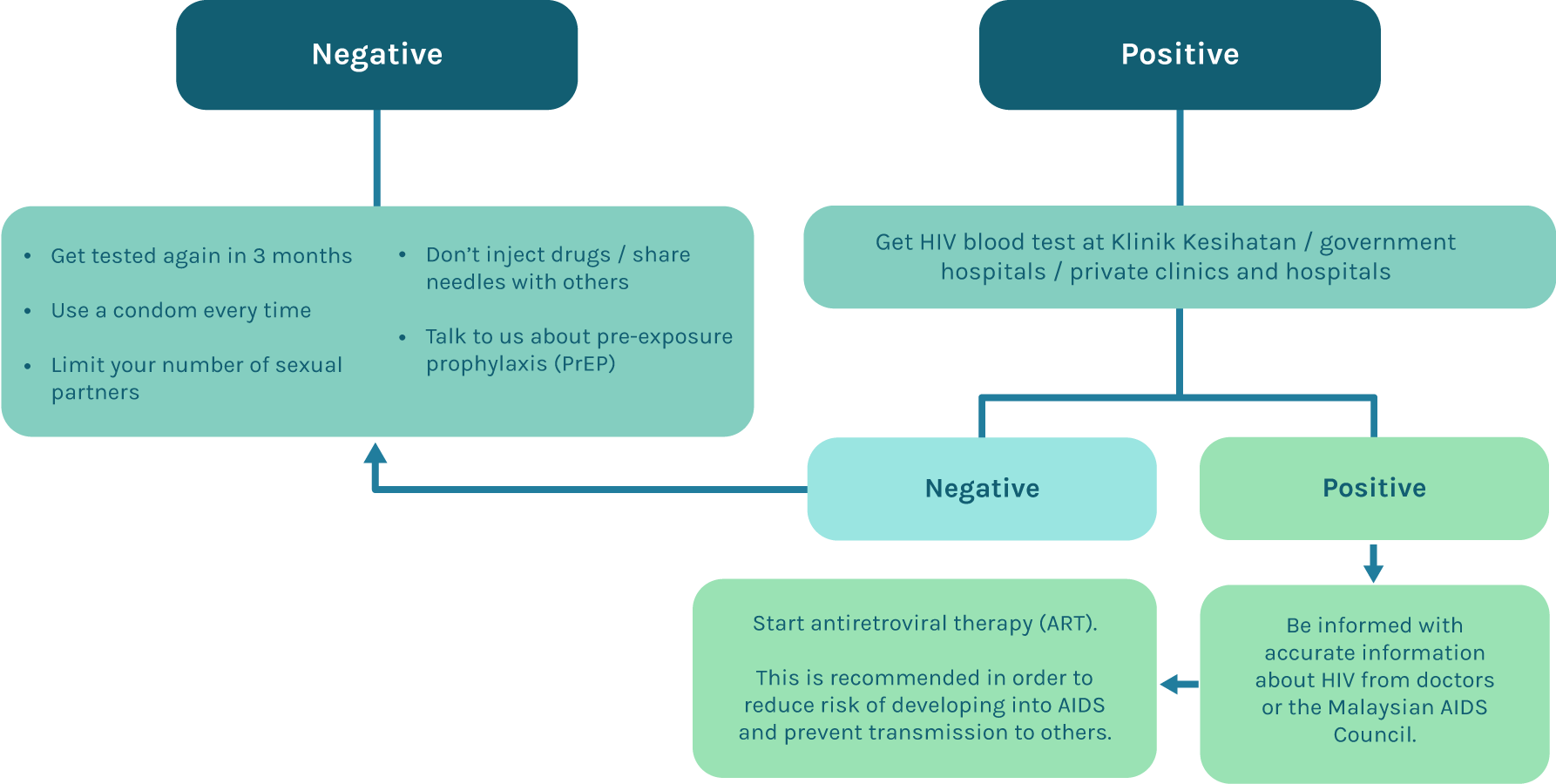
The screening method is a confidential HIV counseling and voluntary testing programme that aims to detect HIV infection and treat it. Rapid test methods will be used and your HIV status is determined within 15 minutes.
If the test result is “Reactive”
- your blood sample will be sent to the HIV Screening Center (Hospital Laboratory) for confirmation testing
- Counseling sessions are conducted by a medical officer or counselor (Information on HIV/AIDS is given)
- Counselor will ask for informed consent before performing an HIV screening test
- On the scheduled consultation date (eg. 2 weeks after the blood sample is taken), you are required to see a medical officer to get the test results and post-test counseling
- If the HIV result is NEGATIVE, another consultation date for a repeat testing is given.
- If the HIV result is POSITIVE, post-test counseling will also be given by a medical officer followed by a discussion of your treatment regime
Kaedah saringan adalah program kaunseling HIV sulit dan ujian sukarela yang bertujuan untuk mengesan jangkitan HIV dan merawatnya. Kaedah ujian pantas akan digunakan dan status HIV anda ditentukan dalam masa 15 minit.
Jika keputusan ujian adalah "Reaktif"
- sampel darah anda akan dihantar ke Pusat Saringan HIV (Makmal Hospital) untuk ujian pengesahan
- Sesi kaunseling dikendalikan oleh pegawai perubatan atau kaunselor (Maklumat HIV/AIDS diberikan)
- Kaunselor akan meminta persetujuan termaklum sebelum melakukan ujian saringan HIV
- Pada tarikh rundingan yang dijadualkan (cth. 2 minggu selepas sampel darah diambil), anda dikehendaki berjumpa pegawai perubatan untuk mendapatkan keputusan ujian dan kaunseling pasca ujian
- Jika keputusan HIV adalah NEGATIF, tarikh rundingan lain untuk ujian ulangan diberikan
- Jika keputusan HIV adalah POSITIF, kaunseling pasca ujian juga akan diberikan oleh pegawai perubatan diikuti dengan perbincangan rejim rawatan anda
HIV screening and tests can be done for free in any government hospital and Klinik Kesihatans. It can also be done in private settings using rapid test kits that can be purchased in pharmacies or online.
Pemeriksaan dan ujian HIV boleh dilakukan secara percuma di mana-mana hospital kerajaan dan Klinik Kesihatan. Ia juga boleh dilakukan dalam tetapan peribadi menggunakan kit ujian pantas yang boleh dibeli di farmasi atau dalam talian.
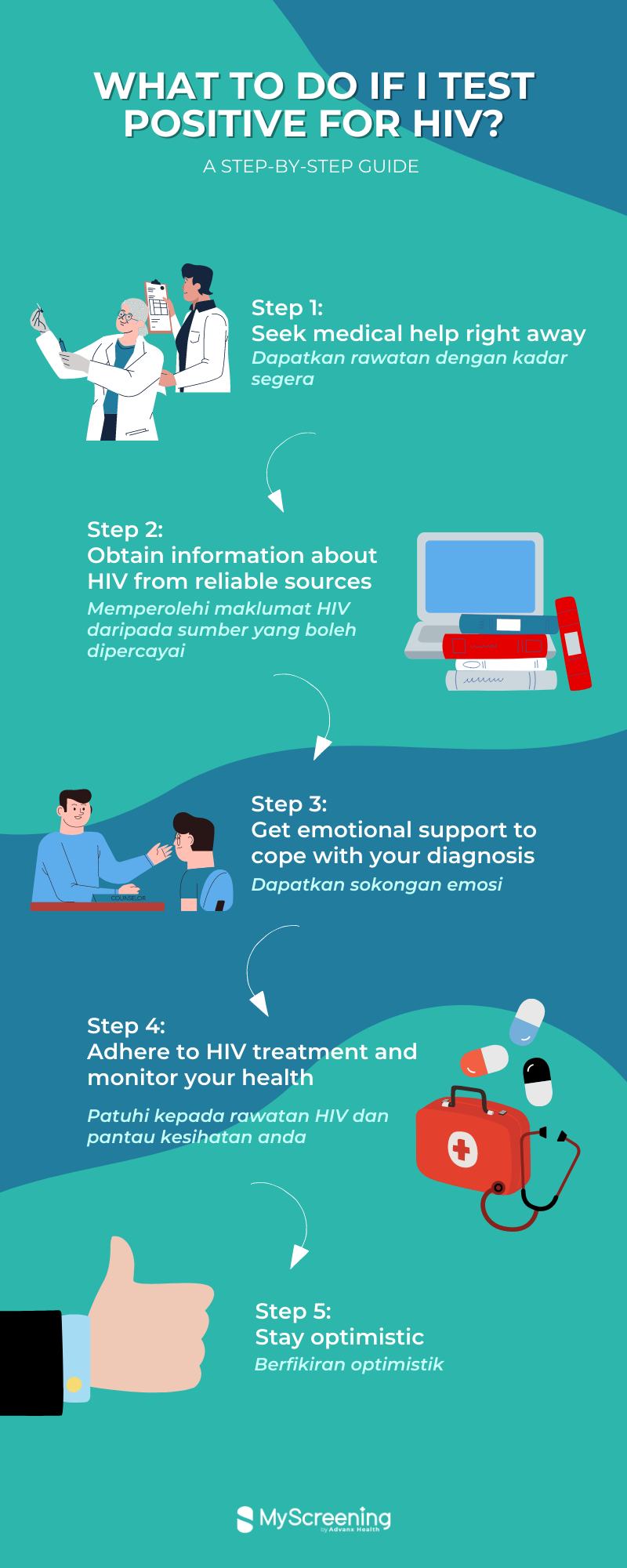
What to do if I test positive for HIV?
Apakah yang sepatutnya saya lakukan jika ujian HIV saya positif?
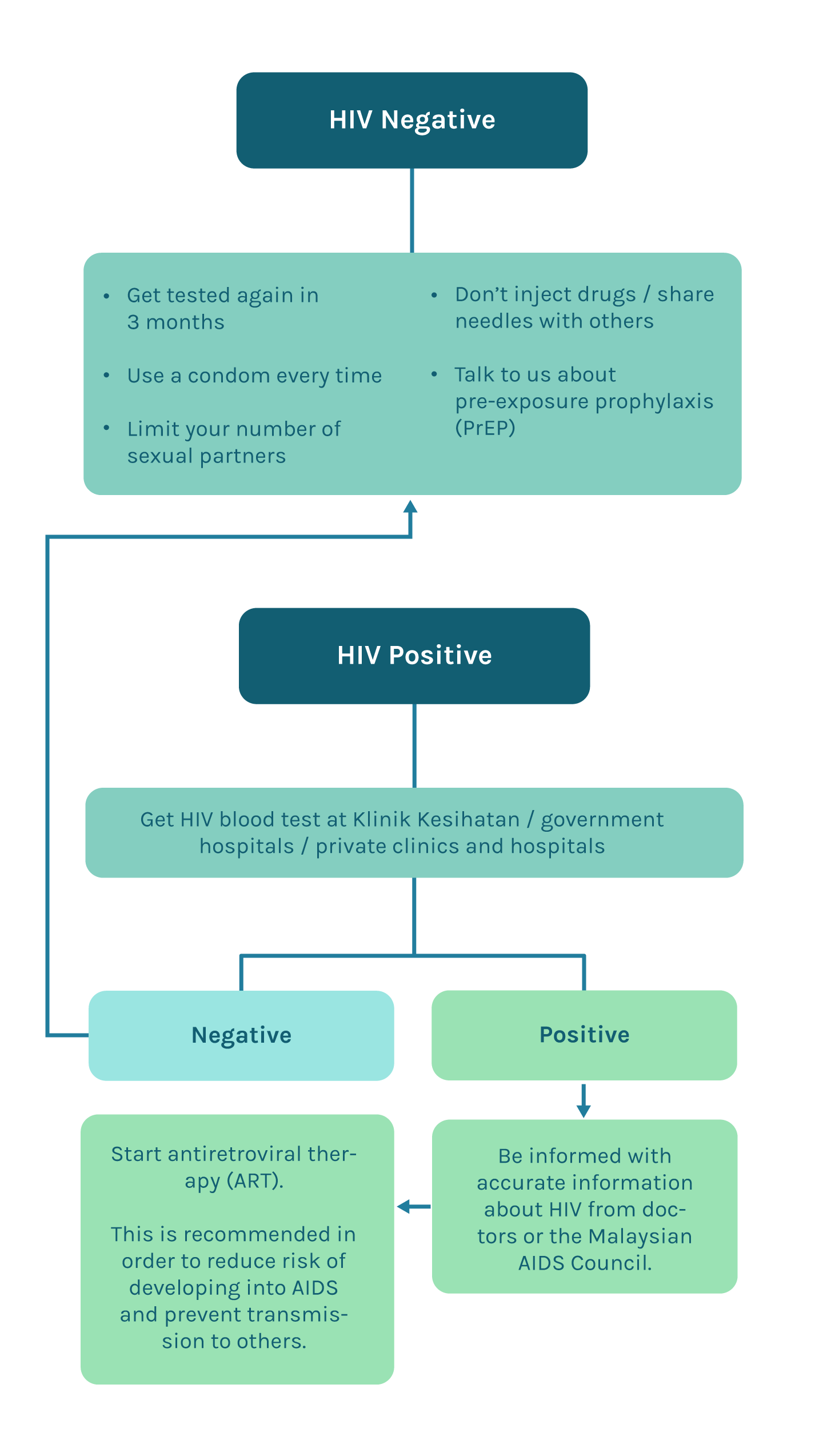
Step 1 : Seek medical help right away
Langkah 1 : Dapatkan rawatan dengan kadar segera
- Locate a healthcare facility in your area and find the right doctor for you. HIV tests and treatment can be found in almost all Klinik Kesihatan and public hospitals in Malaysia.
Cari lokasi pusat kesihatan yang terdekat dan doktor yang bersesuaian. Ujian saringan dan rawatan HIV boleh didapati di kebanyakan klinik kesihatan dan hospital kerajaan di Malaysia. - Feel free to contact us if you need us to refer you to the right medical resources.
Hubungi kami sekiranya anda memerlukan rujukan kepada rawatan yang sesuai.
Step 2 : Obtain information about HIV from reliable sources
Langkah 2 : Memperolehi maklumat tentang HIV daripada sumber yang boleh dipercayai.
- Counseling process with a doctor at the Infectious Disease Division at government hospitals.
Proses kaunseling dengan doktor di bahagian kawalan penyakit berjangkit di hospital kerajaan. - Contact Malaysian AIDS Council.
Hubungi Malaysian AIDS Council.
Step 3 : Get emotional support to cope with your diagnosis
Langkah 3 : Dapatkan sokongan emosi
- Seek local HIV-positive support groups.
Cari kumpulan sokongan HIV tempatan.
eg. TemanTeman.org Malaysia, PT Foundation, Kuala Lumpur AIDS Support Services Society (KLASS)
- Ask your doctor for referral to a mental health professional if needed.
Minta rujukan pesakit daripada doktor anda kepada pakar psikologi jika diperlukan. - Talk to friends and family.
Dapatkan sokongan dari rakan dan ahli keluarga.
Step 4 : Adhere to HIV treatment and monitor your health from time to time
Langkah 4 : Patuhi kepada rawatan HIV dan pantau kesihatan anda dari semasa ke semasa
- Seek local HIV-positive support groups.
Cari kumpulan sokongan HIV tempatan.
eg. TemanTeman.org Malaysia, PT Foundation, Kuala Lumpur AIDS Support Services Society (KLASS)
- Take your medications as prescribed on time.
Ambil ubat tepat pada masa. - Get tested to track your HIV viral load and CD4 count.
Jalani ujian untuk memantau bacaan virus dan sel CD4 anda.
Step 5 : Stay optimistic
Langkah 5 : Berfikiran optimistik
Bear in mind that you still can live a normal life by undergoing antiretroviral therapy and taking good care of your overall health.
Bear in mind that you still can live a normal life by undergoing antiretroviral therapy and taking good care of your overall health.
HIV Treatment and Cure /
Rawatan dan Penawar HIV
Researchers are looking into possible treatments for HIV such as stem cell therapy that could eliminate HIV from infected individuals, and do not have to rely on medications in the future. In the meantime, medication can control the infection and prevent the progression of the disease.
- Medications that can control HIV and prevent complications are called antiretroviral therapy (ART)
- Taking HIV medicine as prescribed stops the progression of the disease to AIDS
- Without medication,HIV will definitely progress to AIDS in a few years time
Penyelidik sedang mengkaji kemungkinan rawatan untuk HIV seperti terapi sel stem yang boleh menghapuskan HIV daripada individu yang dijangkiti, dan tidak perlu bergantung kepada ubat-ubatan pada masa hadapan. Sementara itu, ubat boleh mengawal jangkitan dan mencegah perkembangan penyakit.
- Ubat-ubatan yang boleh mengawal HIV dan mencegah komplikasi dipanggil terapi antiretroviral (ART)
- Pengambilan ubat HIV seperti yang ditetapkan menghentikan perkembangan penyakit kepada AIDS
- Tanpa ubat, HIV pasti akan menjadi AIDS dalam masa beberapa tahun
Antiretroviral therapy (ART)
- ART is usually a combination of two or more medications from several different drug classes
- Anyone that is diagnosed with HIV should be started on HIV, regardless of the stages of infection and CD4 cell count
- There are many ART options that combine multiple HIV medications into one pill, taken once daily
- Each class of drugs blocks the virus in different ways. The function of the classes of drugs:
- Account for individual drug resistance (viral genotype)
- Avoid creating new drug-resistant strains of HIV
- Maximize suppression of the virus in the blood
- ART is effective if it is taken as prescribed, without skipping any doses
- Receiving ART with an undetectable viral load helps to:
- Maintain a strong immune system
- Reduce chances of infection
- Reduce chances of developing treatment-resistant HIV
- Reduce chances of transmitting HIV to others
- People who are taking ART and are virally suppressed do not transmit HIV to their sexual partners
- It is also important to follow up with your health care provider to monitor your health and response to the treatment
Terapi antiretroviral (ART)
- ART biasanya merupakan gabungan dua atau lebih ubat daripada beberapa kelas ubat yang berbeza
- Sesiapa sahaja yang didiagnosis dengan HIV harus dimulakan dengan HIV, tanpa mengira peringkat jangkitan dan kiraan sel CD4
- Terdapat banyak pilihan ART yang menggabungkan beberapa ubat HIV ke dalam satu pil, diambil sekali sehari
- Setiap kelas ubat menyekat virus dengan cara yang berbeza. Fungsi kelas ubat:
- Akaun untuk rintangan dadah individu (genotip virus)
- Elakkan mencipta strain HIV baru yang tahan dadah
- Memaksimumkan penindasan virus dalam darah
- ART berkesan jika ia diambil seperti yang ditetapkan, tanpa melangkau sebarang dos
- Menerima ART dengan viral load yang tidak dapat dikesan membantu:
- Mengekalkan sistem imun yang kuat
- Mengurangkan kemungkinan jangkitan
- Kurangkan peluang mendapat HIV yang tahan rawatan
- Kurangkan peluang untuk menularkan HIV kepada orang lain
- Orang yang mengambil ART dan ditindas secara virus tidak boleh merebak HIV kepada pasangan seksual mereka
- Ia juga penting untuk membuat susulan dengan pembekal penjagaan kesihatan anda untuk memantau kesihatan anda dan tindak balas terhadap rawatan
Treatment for HIV in Malaysia is highly subsidized, easily accessible, and effective for stopping the infection from further spreading. ART is given free to HIV patients regardless of CD4 cell count in public healthcare systems (government hospitals and Klinik Kesihatans). You can also receive treatment in private healthcare centres but there may be additional charges.
Rawatan untuk HIV di Malaysia diberi subsidi yang tinggi, mudah diakses dan berkesan untuk menghentikan jangkitan daripada terus merebak. ART diberikan percuma kepada pesakit HIV tanpa mengira jumlah sel CD4 dalam sistem penjagaan kesihatan awam (hospital kerajaan dan Klinik Kesihatan). Anda juga boleh menerima rawatan di pusat penjagaan kesihatan swasta tetapi mungkin terdapat caj tambahan.
Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q)
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a type of virus that causes damages to the body's immune system. When left untreated, the HIV will kill off CD4 cells (a type of white blood cells called T cells that are vital for the immune system), which increases risks of infections and cancers.
If you are sexually active, you should get a HIV test annually, even if you practice protected sex. If you have had unprotected sex or shared a needle with someone else, you should speak to a medical professional immediately.
One thing to note would be window periods for the detection of HIV in different test methods. For instance, fourth generation tests can detect HIV within four weeks of transmission, while third generation tests detect HIV after 3+ months of transmission. Thus, individuals are always recommended to do a re-test after 3 months for higher accuracy.
No. Only 10μl of blood sample is needed - equivalent to 0.01ml.
Users will be required to use a lancet or sterilized needle to prick their fingers to collect a small amount of blood sample. While every individual has different pain tolerance, the pain that can be felt when getting stung with a new lancet can be compared to an ant bite.
You can purchase HIV test kit at this HIV Test Kit Page
Reference
- First-in-human clinical trial confirms new HIV vaccine approach. Scripps Research Institute. (2021). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/02/210203162249.htm
- HIV/AIDS. Mayoclinic.org. (2020). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hiv-aids/symptoms-causes/syc-20373524
- HIV/AIDS: The basics. Malaysian AIDS Council. (n.d.). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.mac.org.my/v3/i-want-to-learn-more-about-hivaids/
- HIV and AIDS. NHS UK. (2020). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hiv-and-aids/
- HIV treatment. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/basics/livingwithhiv/treatment.html
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. (2019). Global AIDS Monitoring 2020. https://www.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/Laporan/Umum/Laporan_Global_AIDS_Monitoring_2020_new.pdf
- Symptoms and stages of HIV infection. Avert.org. (2020). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.avert.org/about-hiv-aids/symptoms-stages
- What are HIV and AIDS? HIV.gov. (2021). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/about-hiv-and-aids/what-are-hiv-and-aids
- Cardo DM, Culver DH, Ciesielski CA, et al. A case-control study of HIV seroconversion in health care workers after percutaneous exposure. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Needlestick Surveillance Group. N Engl J Med. (n.d.). 1997;337(21):1485–1490.
- DeHaan E, McGowan JP, Fine SM, et al. PEP to Prevent HIV Infection [Internet]. Baltimore (MD): Johns Hopkins University. (2021). Retrieved August 03, 2022, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562734/
- First-in-human clinical trial confirms new HIV vaccine approach. Scripps Research Institute. (2021). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/02/210203162249.htm
- HIV and AIDS. NHS UK. (2020). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hiv-and-aids/
- HIV treatment. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/basics/livingwithhiv/treatment.html
- HIV/AIDS. Mayoclinic.org. (2020). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hiv-aids/symptoms-causes/syc-20373524
- HIV/AIDS: The basics. Malaysian AIDS Council. (n.d.). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.mac.org.my/v3/i-want-to-learn-more-about-hivaids/
- Koh, Kwee. Malaysian Consensus Guidelines on Antiretroviral Therapy 2017. MINISTRY OF HEALTH MALAYSIA. (2017).
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. (2019). Global AIDS Monitoring 2020. https://www.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/Laporan/Umum/Laporan_Global_AIDS_Monitoring_2020_new.pdf
- PEP (post exposure Prophylaxis for HIV). Terrence Higgins Trust. (n.d.). Retrieved August 03, 2022, from https://www.tht.org.uk/hiv-and-sexual-health/pep-post-exposure-prophylaxis-hiv
- Pett, William. What are the side effects of post exposure prophylaxis (PEP)? Nam aidsmap. (2019). Retrieved August 03, 2022, from https://www.aidsmap.com/about-hiv/what-are-side-effects-post-exposure-prophylaxis
- Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (n.d.). Retrieved August 03, 2022, from https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/risk/prep/index.html
- PrEP for HIV Prevention, the pill that keeps you HIV negative. Ending HIV. (n.d.). Retrieved August 03, 2022, from https://endinghiv.org.au/stay-safe/prep/
- Symptoms and stages of HIV infection. Avert.org. (2020). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.avert.org/about-hiv-aids/symptoms-stages
- What are HIV and AIDS? HIV.gov. (2021). Retrieved April 01, 2021, from https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/about-hiv-and-aids/what-are-hiv-and-aids
- HIV. (2022, July 27). Retrieved September 8, 2022, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids
- HIV Basics. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2022, from https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/basics/
- HIV: PrEP and PEP. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2022, from https://medlineplus.gov/hivprepandpep.html
- HIV Testing. What Test Is Used To Screen For HIV? . (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2022, from https://www.doctoroncall.com.my/health-centre/hiv-aids/hiv-test
- HIV/AIDS - Diagnosis and treatment. (2022, July 29). Retrieved September 8, 2022, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hiv-aids/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20373531
- Pap Smears and HIV Detection. (2020, June 12). Retrieved September 8, 2022, from https://www.webmd.com/hiv-aids/pap-smear-detect-hiv
- Preventing Sexual Transmission of HIV. (2022, July 20). Retrieved September 8, 2022, from https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/hiv-prevention/reducing-sexual-risk/preventing-sexual-transmission-of-hiv
- What Are HIV and AIDS? (2022, July 20). Retrieved September 8, 2022, from https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/about-hiv-and-aids/what-are-hiv-and-aid